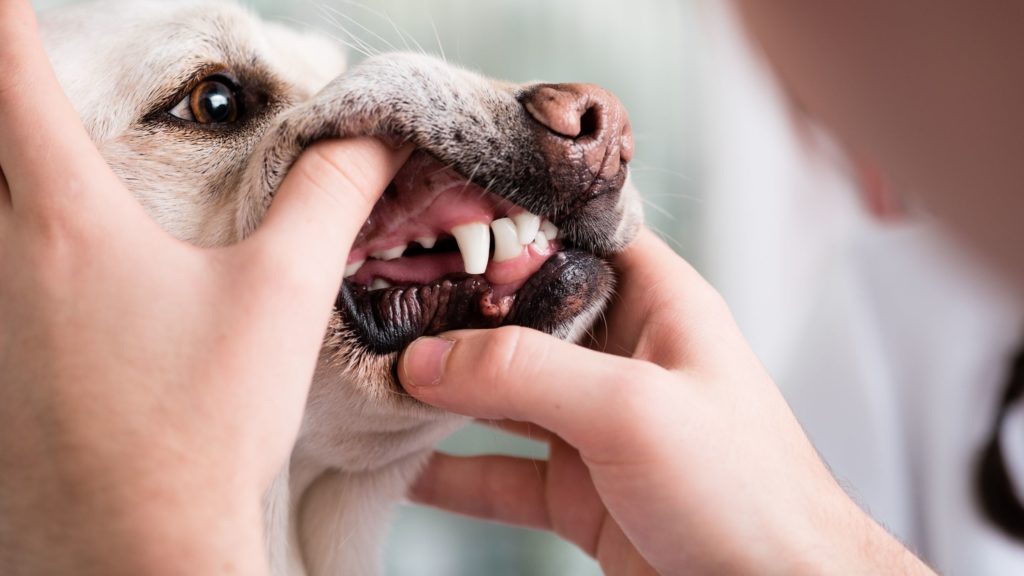
Es la eliminación del sarro y la placa adherida a la superficie de los dientes mediante un equipo de ultrasonidos que garantiza la integridad de las piezas dentales a la vez que elimina en profundidad cualquier resto de suciedad.
A continuación se procede al pulido de los dientes mediante una fresa especial que elimina la placa bacteriana y devuelve a los dientes el aspecto sano que deben tener.
Una vez terminado todo el proceso, se mantiene al perro en observación hasta que se despierta de la anestesia, bajo la atenta supervisión de un veterinario.
¿Cada cuánto tiempo tengo que hacerle una limpieza dental a mi perro?
A partir de cierta edad, los perros pueden necesitar una limpieza dental anual o bianual. Depende de cada caso. En líneas generales, puede decirse que los perros de razas pequeñas suelen acumular más sarro y suelen necesitar una atención mayor en cuanto a higiene dental.
Riesgos de una mala higiene
Los riesgos más evidentes de una mala higiene dental en los perros son los siguientes:
- Cuando la acumulación de sarro no se trata, se puede producir una inflamación y retracción de las encías que puede descalzar el diente y provocar caídas.
- Mal aliento (halitosis).
- Sarro perros
- Puede ir a más
- Las bacterias de la placa pueden trasladarse a través del torrente circulatorio a órganos vitales como el corazón ocasionando problemas de endocarditis en las válvulas. Las bacterias pueden incluso acantonarse en huesos (La osteomielitis es la infección ósea, tanto cortical como medular) provocando mucho dolor y una artritis séptica).
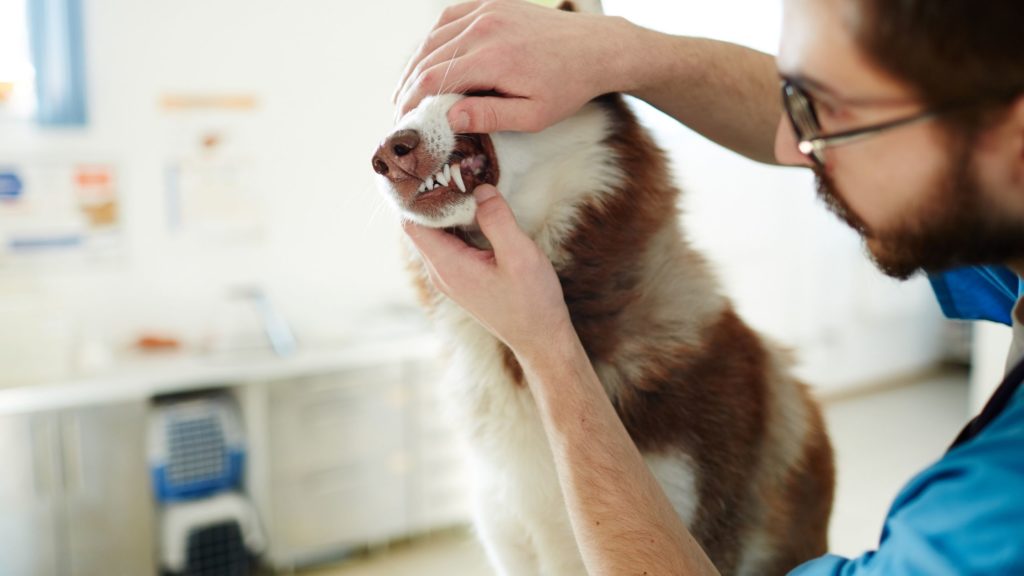
¿Cómo se forma el sarro?
El sarro es la calcificación de la placa dental. Los restos de alimentos, junto con las bacterias presentes en la boca, van a formar la placa bacteriana o placa dental. Si la placa no se retira, al mezclarse con la saliva y los minerales presentes en ella, reaccionará formando una costra. La placa se calcifica y se forma el sarro.
El sarro, cuando se forma, es de color blanquecino pero a medida que pasa el tiempo se va poniendo amarillo y luego marrón.
Síntomas de una pobre higiene dental
La señal más obvia de una mala salud dental canina es el mal aliento.
Sin embargo, a veces no es tan fácil de detectar
Y hay perros que no se dejan abrir la boca por su dueño. Por ejemplo…
Recientemente nos trajeron a la clínica a un perro que parpadeaba de un ojo y decía su dueño que le picaba un lado de la cara. Tenía molestias y dificultad para comer, lo que había llevado a sus dueños a comprarle comida blanda (que suele ser un poco más cara y llevar más contenido en grasa) durante medio año. Después de una exploración oftalmológica, nos dimos cuenta de que el ojo tenía una úlcera en la córnea probablemente de rascarse . Además, el canto lateral del ojo estaba inflamado. Tenía lo que en humanos llamamos flemón pero como era un perro de pelo largo, no se le notaba a simple vista. Al abrirle la boca nos llamó la atención el ver una muela llena de sarro. Le realizamos una radiografía y encontramos una fístula que llegaba hasta la parte inferior del ojo.
Le tuvimos que extraer la muela. Tras esto, el ojo se curó completamente con unos colirios y una lentilla protectora de úlcera. Afortunadamente, la úlcera no profundizó y no perforó el ojo. Ahora el perro come perfectamente a pesar de haber perdido una muela.
¿Cómo mantener la higiene dental de tu perro?
Hay varias maneras de prevenir problemas derivados de la salud dental de tu perro.
Limpiezas de dientes en casa
Es recomendable limpiar los dientes de tu perro semanal o diariamente si se puede. Existe una gran variedad de productos que se pueden utilizar:
Pastas de dientes.
Cepillos de dientes o dedales para el dedo índice, que hacen más fácil la limpieza.
Colutorios para echar en agua de bebida o directamente sobre el diente en líquido o en spray.
En la Clínica Tus Veterinarios enseñamos a nuestros clientes a tomar el hábito de limpiar los dientes de sus perros desde que son cachorros. Esto responde a nuestro compromiso con la prevención de enfermedades caninas.
Hoy en día tenemos muchos clientes que limpian los dientes todos los días a su mascota, y como resultado, se ahorran el dinero de hacer limpiezas dentales profesionales y consiguen una mejor salud de su perro.
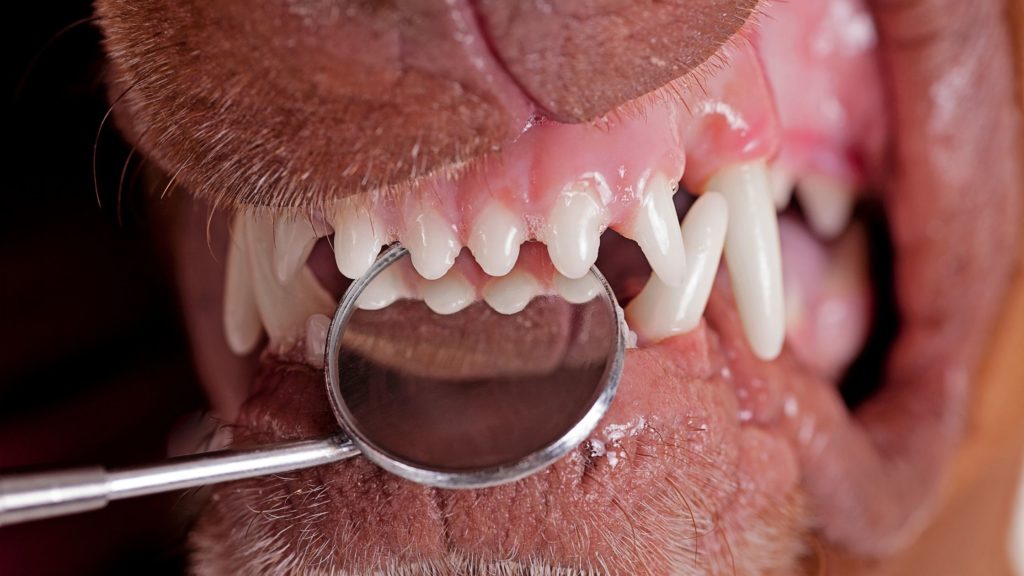
Limpiezas dentales profesionales de perros y gatos
Recomendamos hacer una limpieza dental especializada anualmente. La realizamos con un aparato de ultrasonidos que utiliza agua para quitar el sarro. Después, procedemos a pulir los dientes con un cepillo de alta velocidad y una pasta especial. Hacemos esto para proteger el esmalte.
La frecuencia de limpiezas dentales necesaria varía mucho entre razas. En general, las razas grandes tienen buena calidad de esmalte, por lo que no necesitan hacerlo tan a menudo e incluso pueden pasarse la vida sin requerir una limpieza. Sin embargo, razas pequeñas como el Yorkshire o el Maltés, deben hacérselas todos los años desde cachorros si se quiere conservar sus piezas dentales.
Otro factor fundamental es la calidad del pienso. Algunas marcas han diseñado croquetas que limpian la superficie del diente y de la muela al masticarse.
Ultrasonido para perros
¿Se necesita anestesia para las limpiezas dentales de perros y gatos?
La limpieza dental en perros no es una técnica que pueda practicarse sin anestesia general , aunque hay veces que los propietarios no quieren anestesiar y si tiene poco sarro y el perro es muy bueno se puede intentar…… , pero no se va a poder pulir ni acceder a todas la zona de la boca …. Además los limpiadores dentales van a irrigar agua y hay riesgo de aspiración a vías respiratorias si no se realiza una anestesia correcta con intubación traqueal . En resumen , sin anestesia no se va hacer una correcta limpieza dental.
Tampoco sirve la sedación ya que necesitamos que el animal esté totalmente quieto, y el veterinario tenga un acceso completo a todas sus piezas dentales y encías.
Alimentos para la limpieza dental
Hay que tener cierto cuidado a la hora de comprar determinados alimentos porque no todos son saludables. Algunos tienen demasiado contenido graso, que en exceso puede causar problemas cardiovasculares y obesidad.
Los mejores alimentos para los dientes son aquellos que están elaborados por empresas farmacéuticas y llevan componentes químicos con tratamientos específicos para el diente del perro. Esto implica no solo limpieza a través de la acción mecánica de morder sino también un tratamiento antibacteriano para prevenir el sarro.
Conclusión
Si eres como la mayoría de dueños, por falta de tiempo , es probable que no estés prestando la suficiente atención a la limpieza dental de tu perro. Por eso te animamos a que comiences a limpiar los dientes de tu perro y consideres atender a su higiene bucal con frecuencia.
Estas simples medidas pueden conllevar a que tu perro tenga una vida más larga y mucho más saludable.
Si te resulta imposible introducir un cepillo de dientes a tu perro en la boca, pásate con él por clínica Tus Veterinarios y te explicamos cómo hacerlo.
Necesitas hacer una limpieza dental profesional a tu mascota?
Llámanos al 622575274 o contacta con nosotros

